Relationships
Contexts can relate to each other. A customer context can have many order contexts. An order context can belong to a customer. These relationships let you build decisions that span multiple entities.
The Pattern
Customer (one) → Orders (many)
A customer context tracks lifetime data: total spend, order count, loyalty tier. Each order context tracks a single transaction. When an order completes, you might want to update the customer's lifetime stats.
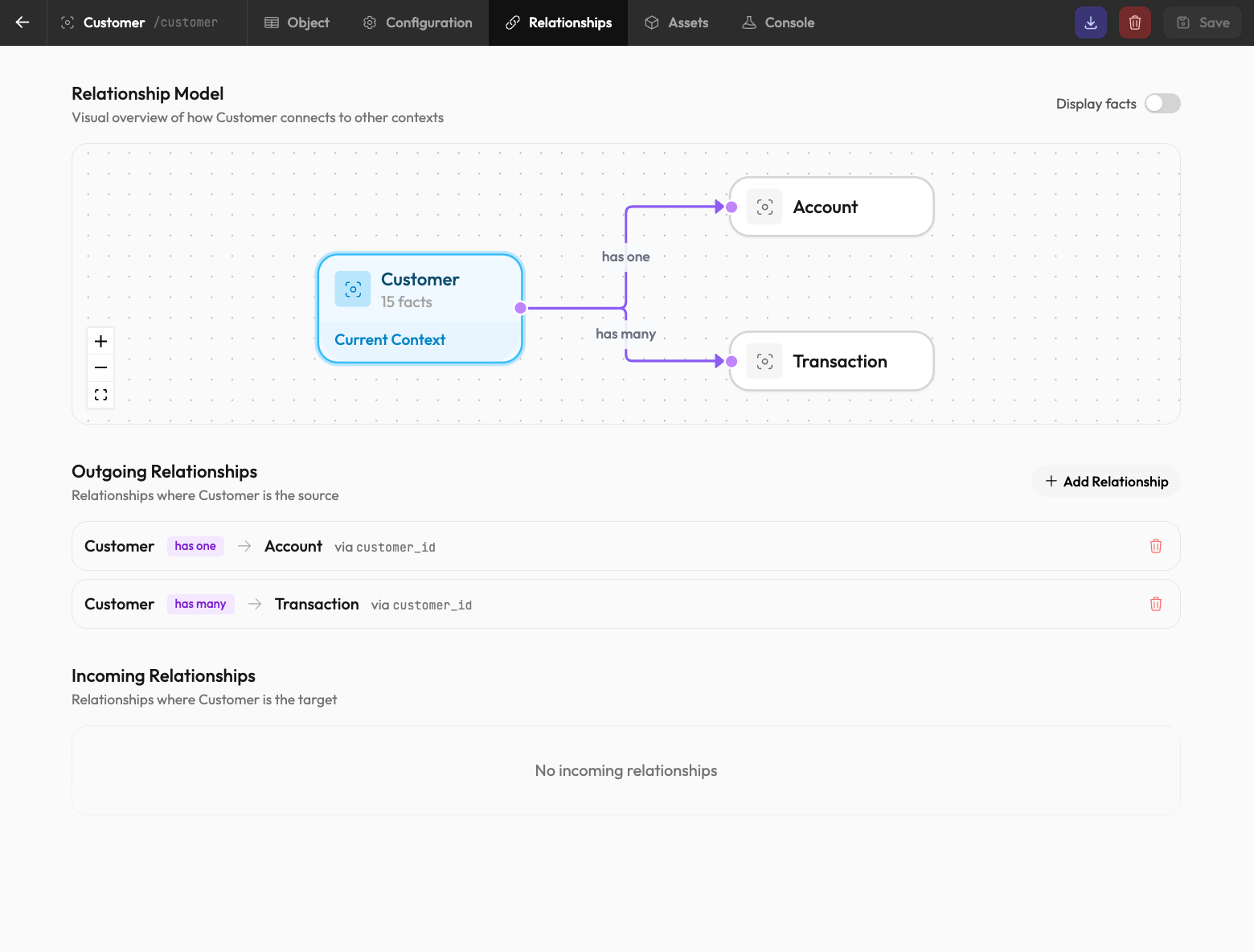
Defining Relationships
In the Context Editor, add a relationship field:
On the Customer context:
orders: has_many(Order, 'customer_id')On the Order context:
customer_id: string (foreign key)Now orders link to their customer, and customers can reference their orders.
Using Relationships in Derived Facts
The power shows up in derived facts. On the Customer context:
// Total spend across all orders
total_spend: sum($relations.orders, 'total')
// Number of completed orders
order_count: count($relations.orders, 'status == "complete"')
// Most recent order date
last_order_date: max($relations.orders, 'created_at')These recalculate automatically when any related order changes.
Cascading Across Relationships
When an order is marked complete, it can trigger rules on the customer context:
- Order context receives
status: "complete" - Customer's
order_countderived fact recalculates - If
order_countcrosses a threshold, a loyalty tier rule executes - Customer's
loyalty_tierfact updates
This cascade happens automatically based on the relationships and rule bindings you've defined.
Relationship queries ($relations.orders) only include live, non-expired context instances. Expired orders won't appear in aggregations.
Navigating the Other Direction
From an order, access the parent customer:
// Get customer's tier for order-level pricing
customer_tier: $relations.customer.loyalty_tierThis creates a dependency—the order context waits for the customer's loyalty_tier before derived facts using it can calculate.